The ketogenic diet has gained popularity for its potential benefits in weight loss, blood sugar control, and metabolic health. When done correctly, keto can also support brain function by providing ketones as an alternative fuel source. However, when the ketogenic diet is poorly planned or followed incorrectly, it may negatively impact brain health. This article explains how keto done wrong can affect the brain, the common mistakes people make, and how to follow keto safely and effectively.
How the Brain Uses Energy
The brain primarily relies on glucose for energy, but during ketosis it can efficiently use ketones. This metabolic flexibility can be beneficial. Problems arise when nutrient intake, hydration, and overall balance are neglected.
Ways Keto Done Wrong Can Damage Brain Health
1. Severe Calorie Restriction
Extremely low calorie intake while on keto can deprive the brain of essential energy. Chronic under-eating may lead to brain fog, dizziness, poor concentration, and mood disturbances.
2. Electrolyte Imbalance
Low-carb diets cause increased water and electrolyte loss. Without adequate sodium, potassium, and magnesium, the nervous system can suffer, leading to headaches, confusion, anxiety, and fatigue.
3. Lack of Essential Nutrients
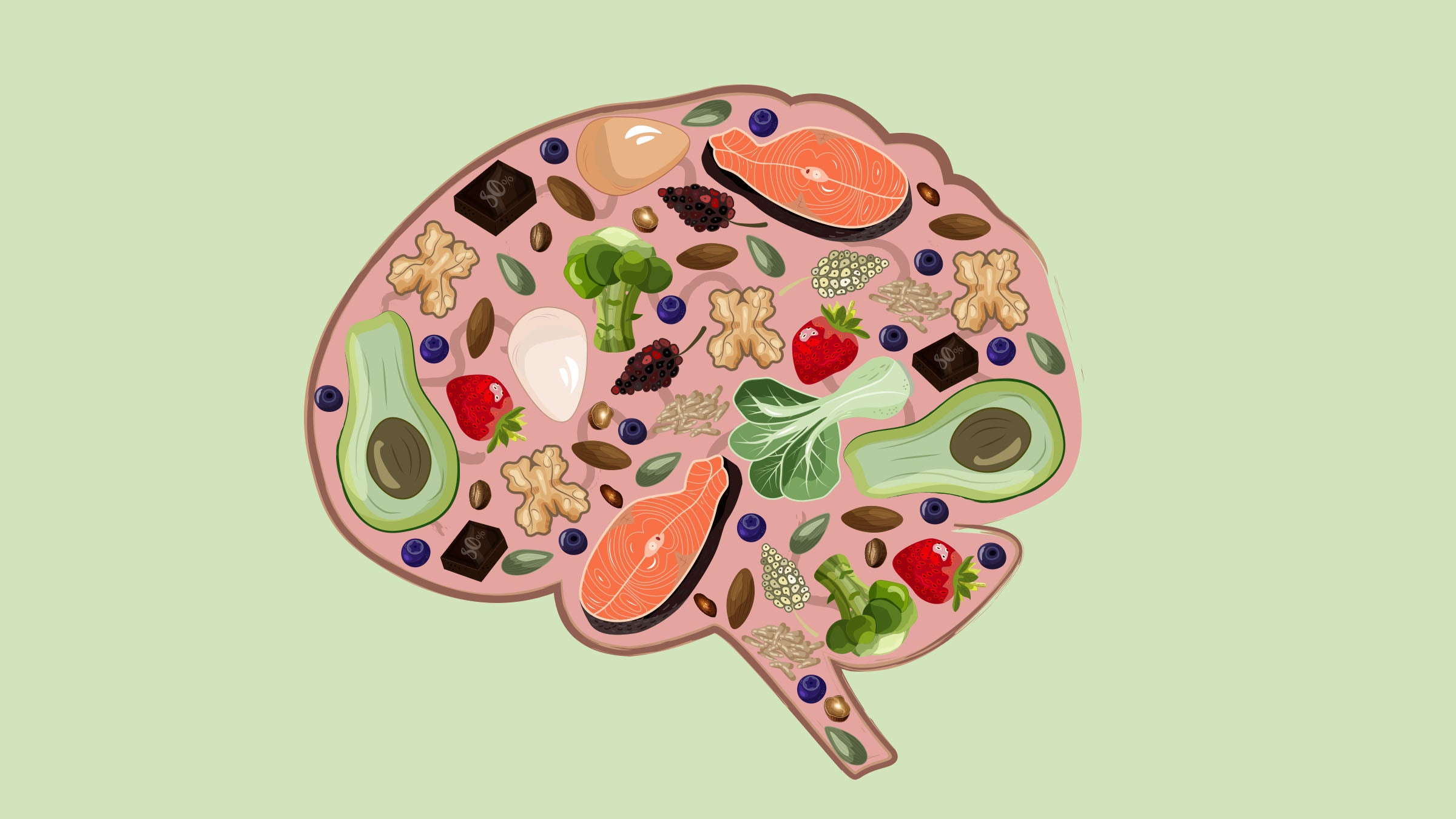
Poorly planned keto diets may lack B vitamins, omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and minerals necessary for neurotransmitter production and brain protection. Nutrient deficiencies over time can impair cognitive function.
4. Excessive Saturated and Processed Fats
Relying heavily on processed meats and low-quality fats may increase inflammation and oxidative stress, which are linked to impaired brain health and cognitive decline.
5. Inadequate Protein Intake
Too little protein can reduce the availability of amino acids needed for neurotransmitters such as dopamine and serotonin, affecting mood, memory, and focus.
6. Chronic Stress and Hormonal Disruption
Over-restrictive keto combined with intense exercise or poor sleep can elevate cortisol levels. Chronically high cortisol negatively affects memory, learning, and emotional regulation.
Warning Signs Keto May Be Affecting Your Brain
- Persistent brain fog
- Memory issues
- Difficulty concentrating
- Mood swings or irritability
- Anxiety or depressive symptoms
- Frequent headaches
How to Do Keto Safely for Brain Health
- Eat enough calories to support daily energy needs
- Prioritize whole-food fat sources such as olive oil, avocados, nuts, seeds, and fatty fish
- Include adequate protein from quality sources
- Replace electrolytes daily, especially sodium and magnesium
- Eat low-carb vegetables to support micronutrient intake
- Avoid long-term extreme restriction without professional supervision
Who Should Be Especially Careful
Individuals with a history of eating disorders, chronic stress, thyroid disorders, or neurological conditions should approach keto cautiously and seek medical guidance before starting.
The ketogenic diet is not inherently harmful to the brain, but when done incorrectly, it can lead to nutrient deficiencies, hormonal imbalances, and cognitive symptoms. A well-formulated keto approach that prioritizes nutrition, balance, and sustainability is essential for protecting both brain health and overall well-being.



